linux內(nèi)核中的文件描述符(一)--基礎(chǔ)知識(shí)簡介
CPU architecture:ARM920T
本文引用地址:http://www.104case.com/article/201611/319997.htmAuthor:ce123(http://blog.csdn.net/ce123)
作為文件的使用者,進(jìn)程理所當(dāng)然的要將所使用的文件記錄于自己的控制塊中,也就是task_struct。另外,由于進(jìn)程所對應(yīng)的程序也是一個(gè)文件,因此進(jìn)程控制塊還必須記錄這個(gè)文件的相關(guān)信息。由于OS要對所有進(jìn)程提供服務(wù),因此OS還要維護(hù)一個(gè)記錄所有進(jìn)程打開的文件的總表。
1.文件對象
當(dāng)進(jìn)程通過open系統(tǒng)調(diào)用打開一個(gè)文件時(shí),該系統(tǒng)調(diào)用找到這個(gè)文件后,會(huì)把文件封裝到一個(gè)file結(jié)構(gòu)的實(shí)例中提供給進(jìn)程,這個(gè)實(shí)例稱為file對象。file結(jié)構(gòu)的定義如下:
- structfile{
- structlist_headf_list;//所有打開文件的鏈表
- structdentry*f_dentry;//文件的dentry
- structvfsmount*f_vfsmnt;//文件目錄的VFS安裝點(diǎn)指針
- structfile_operations*f_op;//指向文件操作函數(shù)集的指針
- atomic_tf_count;//記錄訪問本文件的進(jìn)程數(shù)目的計(jì)數(shù)器
- unsignedintf_flags;//訪問類型
- mode_tf_mode;//訪問模式
- loff_tf_pos;//文件當(dāng)前的讀寫位置
- structfown_structf_owner;
- unsignedintf_uid,f_gid;//文件所有者ID和用戶組ID
- structfile_ra_statef_ra;
- unsignedlongf_version;
- void*f_security;
- /*neededforttydriver,andmaybeothers*/
- void*private_data;
- #ifdefCONFIG_EPOLL
- /*Usedbyfs/eventpoll.ctolinkallthehookstothisfile*/
- structlist_headf_ep_links;
- spinlock_tf_ep_lock;
- #endif/*#ifdefCONFIG_EPOLL*/
- structaddress_space*f_mapping;
- structrcu_headf_rcuhead;
- };
結(jié)構(gòu)中的域f_uid為文件所有者的ID,f_gid為文件所有者所在組的ID。這樣就使得一個(gè)文件可能面臨三種用戶的訪問:
- 文件所有者;
- 同組用戶;
- 其他用戶。
內(nèi)核在處理一個(gè)進(jìn)程或用戶訪問一個(gè)文件的請求時(shí),要根據(jù)進(jìn)程的f_uid和f_gid以及訪問模式來確定該進(jìn)程是否具有訪問這個(gè)文件的權(quán)限。對于一個(gè)用戶來說,可以有讀、寫和執(zhí)行三種文件權(quán)限,這三種權(quán)限和三種用戶就共有9中組合,即文件的訪問權(quán)限可以用9個(gè)bit來表示,并將其保存在文件的dentry中。
結(jié)構(gòu)中的域f_pos記錄了進(jìn)程對文件讀寫位置的當(dāng)前值,可以通過調(diào)用函數(shù)llseek進(jìn)程移動(dòng)。
結(jié)構(gòu)中的f_op執(zhí)向結(jié)構(gòu)file_operations,該結(jié)構(gòu)封裝了對文件進(jìn)行操作的函數(shù),定義如下:
- structfile_operations{
- structmodule*owner;
- loff_t(*llseek)(structfile*,loff_t,int);
- ssize_t(*read)(structfile*,char__user*,size_t,loff_t*);
- ssize_t(*aio_read)(structkiocb*,char__user*,size_t,loff_t);
- ssize_t(*write)(structfile*,constchar__user*,size_t,loff_t*);
- ssize_t(*aio_write)(structkiocb*,constchar__user*,size_t,loff_t);
- int(*readdir)(structfile*,void*,filldir_t);
- unsignedint(*poll)(structfile*,structpoll_table_struct*);
- int(*ioctl)(structinode*,structfile*,unsignedint,unsignedlong);
- long(*unlocked_ioctl)(structfile*,unsignedint,unsignedlong);
- long(*compat_ioctl)(structfile*,unsignedint,unsignedlong);
- int(*mmap)(structfile*,structvm_area_struct*);
- int(*open)(structinode*,structfile*);
- int(*flush)(structfile*);
- int(*release)(structinode*,structfile*);
- int(*fsync)(structfile*,structdentry*,intdatasync);
- int(*aio_fsync)(structkiocb*,intdatasync);
- int(*fasync)(int,structfile*,int);
- int(*lock)(structfile*,int,structfile_lock*);
- ssize_t(*readv)(structfile*,conststructiovec*,unsignedlong,loff_t*);
- ssize_t(*writev)(structfile*,conststructiovec*,unsignedlong,loff_t*);
- ssize_t(*sendfile)(structfile*,loff_t*,size_t,read_actor_t,void*);
- ssize_t(*sendpage)(structfile*,structpage*,int,size_t,loff_t*,int);
- unsignedlong(*get_unmapped_area)(structfile*,unsignedlong,unsignedlong,unsignedlong,unsignedlong);
- int(*check_flags)(int);
- int(*dir_notify)(structfile*filp,unsignedlongarg);
- int(*flock)(structfile*,int,structfile_lock*);
- };
2.文件描述符
下面進(jìn)一步介紹進(jìn)程對自己所訪問的file對象的管理方法。linux中使用一個(gè)數(shù)組來管理進(jìn)程打開的文件的file對象,數(shù)組中的每個(gè)元素都存放一個(gè)紙箱進(jìn)程所打開的文件的file對象。既然用一個(gè)數(shù)組來存放file對象,那么用數(shù)組的下標(biāo)來訪問文件就是一件順理成章的方法,于是,linux就把數(shù)組元素的下標(biāo)叫做該數(shù)組元素所對應(yīng)的文件的文件描述符,該描述符就是系統(tǒng)對文件的標(biāo)識(shí),這個(gè)數(shù)組也叫文件描述符數(shù)組,如下圖所示:
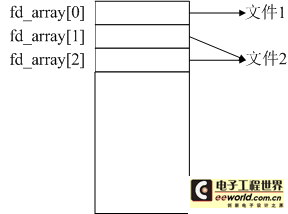
內(nèi)核通過系統(tǒng)調(diào)用dup、dup2和fctl可以使數(shù)組中的多個(gè)元素指向同一個(gè)文件的file對象,也就是說,在linux中,同一個(gè)文件可以有多個(gè)文件描述符。
3.進(jìn)程打開文件表
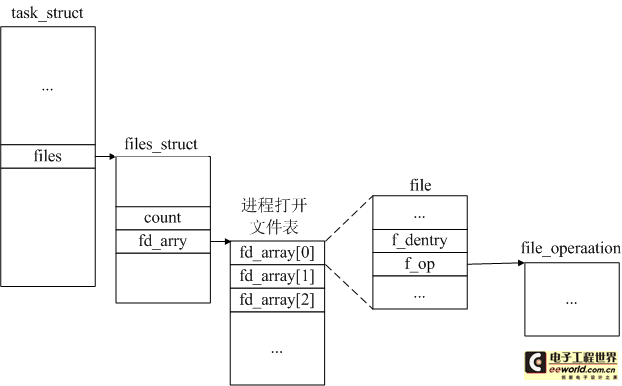
進(jìn)程描述符數(shù)組中存放了一個(gè)進(jìn)程所訪問的所有文件,把這個(gè)文件描述符數(shù)組和這個(gè)數(shù)組在系統(tǒng)中的一些動(dòng)態(tài)信息組合到一起,就形成了一個(gè)新的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)——進(jìn)程打開文件表,即file_struct,其定義如下:
- /*
- *Openfiletablestructure
- */
- structfiles_struct{
- atomic_tcount;//引用計(jì)數(shù)
- spinlock_tfile_lock;/*Protectsallthebelowmembers.Nestsinsidetsk->alloc_lock*/
- structfdtable*fdt;//管理文件描述符
- structfdtablefdtab;//管理文件描述符
- fd_setclose_on_exec_init;//位圖
- fd_setopen_fds_init;//位圖
- structfile*fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT];//文件描述符數(shù)組
- };
- structtask_struct{
- ...
- /*openfileinformation*/
- structfiles_struct*files;
- ...
- };
4.文件描述符的管理
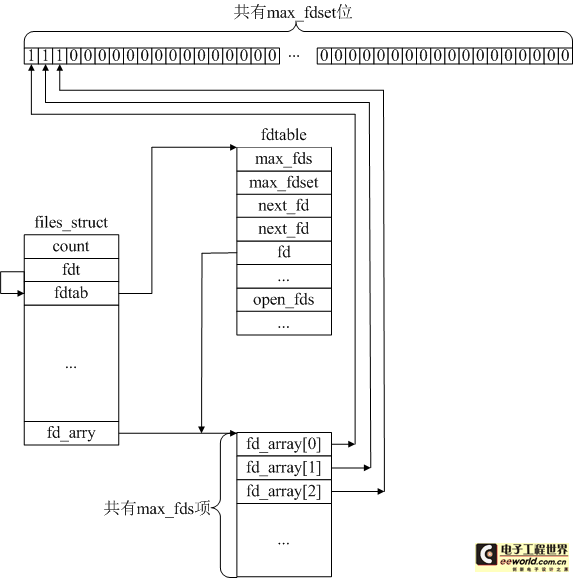
file_struct中的fdt和fdtab用于管理文件文件描述符,一個(gè)是fdtable類型,另一個(gè)是其指針類型。fdtable的定義如下:
- structfdtable{
- unsignedintmax_fds;//可以代開的最大文件數(shù)
- intmax_fdset;//位圖的最大長度
- intnext_fd;//下一個(gè)可用的fd
- structfile**fd;/*currentfdarray指向files_struct的fd_array*/
- fd_set*close_on_exec;
- fd_set*open_fds;//打開的文件標(biāo)記,比如第2位為0,則打開了2號文件
- structrcu_headrcu;
- structfiles_struct*free_files;
- structfdtable*next;
- };
下圖可以很直觀的說明文件描述符fd的管理。



評論